Location of the tonsils
EXCESSIVE GROWTH OF THE ADENOIDS IN CHILDREN IS A FREQUENTLY OBSERVED PHENOMENON
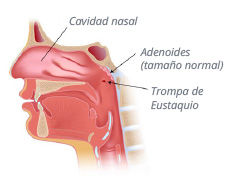
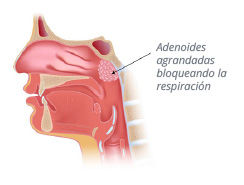
Adenoids and tonsils
Nasal endoscopy
My son snores: Does he have a tonsil problem?
ENLARGED ADENOIDS
Adenoids are masses of tissue that starts to develop during childhood behind the nose, where the nose blends into the throat. This is why their enlargement blocks, either partially or completely interrupts, the air breathed through the nose, causing respiratory problems.
The adenoids start to develop from the age of 6 months.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms can include:
- difficulty breathing through the nose so the child breathes through the mouth. The mouth being constantly open will cause the child to develop distinctive facial features
- snoring (sometime accompanied by sleep apnoea (temporary pauses in breathing))
- nasal catarrh, with frequent discharge from the nose
How are enlarged adenoids treated?
The recommended treatment for enlarged adenoids is their removal. This is performed via a very short procedure (10 minutes) under general anaesthetic. It is usually an outpatient procedure and the patient is allowed home several hours after surgery.
In some cases, surgery will be combined with reduction or removal of the tonsils and/or the insertion of ventilation tubes into the ears.
El niño roncador. El niño con síndrome de apnea obstructiva del sueño.
Dr. Jordi Coromina. Otorrinolaringólogo de Hospital Quirón Teknon.
 by Develona
by Develona